Allergology is a branch of medicine that studies the mechanisms causing allergic diseases and immune disorders, focusing on the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation of patients with such conditions.
Allergic diseases are chronic conditions with complex mechanisms, involving exaggerated reactions of the immune system to substances that are harmless to most people (allergens). They can occur at any age and may significantly affect the patient’s quality of life and even their safety.
The allergist is the specialist who:
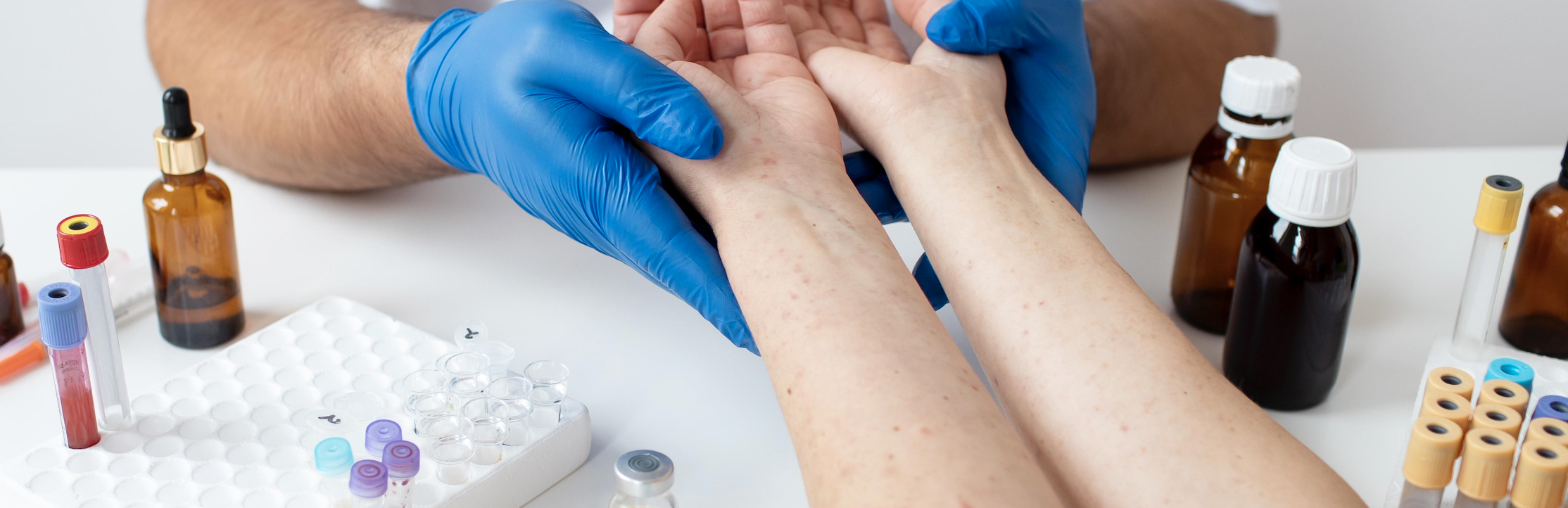
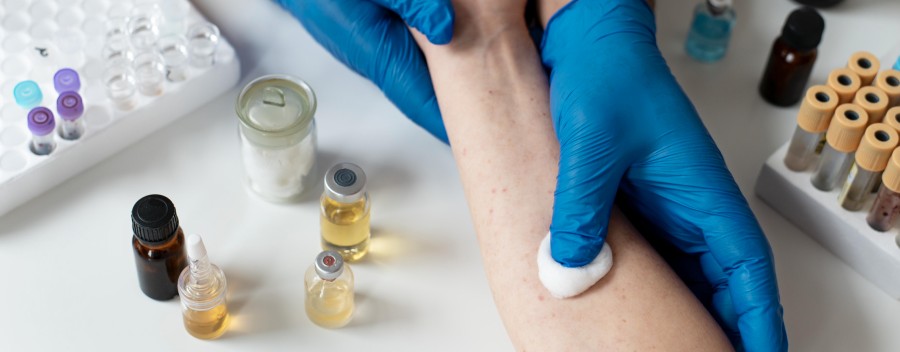
- evaluates and identifies the causes of allergic reactions through specific tests (skin, laboratory, immunological);
- establishes a differential diagnosis between allergic and non-allergic diseases;
- recommends personalized treatments, including allergen-specific immunotherapy;
- monitors the evolution of the disease and provides counseling to prevent relapses;
- educates the patient on avoiding triggers and on self-management of allergic episodes.
The most common allergic conditions include:
- allergic rhinitis and conjunctivitis;
- allergic bronchial asthma;
- atopic dermatitis and contact dermatitis;
- urticaria and angioedema;
- food allergy;
- drug allergy;
- allergy to insect venom;
- anaphylaxis.
An allergology consultation is recommended if the following occur:
- persistent nasal congestion, sneezing, watery discharge, cough, or difficulty breathing;
- skin rashes, hives, eczema, itching;
- unusual reactions after eating certain foods, taking medication, or insect stings;
- episodes of anaphylaxis (severe allergic reaction);
- suspicion of occupational allergy or immunodeficiency.