Tetanus is an infectious disease caused by the neurotoxin of the bacterium Clostridium tetani, which can lead to death in 40–50% of cases. The bacterium Clostridium tetani, found in soil and street dust, enters the body through skin wounds caused by cuts, tears, animal bites, abrasions, or even minor scratches. It multiplies in the wound and releases a neurotoxin that causes the disease. The severe symptoms are characterized by muscle cramps, which in the case of neck muscle spasms can lead to asphyxia.
Transmission
Tetanus is not transmitted from person to person. The disease occurs only in non-immunized individuals after infection of a skin wound, often considered insignificant, caused by sharp or cutting objects contaminated with soil (nails, needles, thorns, splinters, scissors, knives, etc.) or through scratches and animal bites. Burns or frostbite wounds can also serve as an entry point for the tetanus bacillus. Newborns can be infected if the umbilical cord is cut with a non-sterile instrument and/or covered with a non-sterile dressing.
Symptoms
The incubation period ranges from 7 to 10 days. The characteristic symptoms of tetanus include:
- severe muscle stiffness that locks the jaws (lockjaw)
- contraction of the neck and abdominal muscles
- contraction of the back muscles
- difficulty swallowing
- generalized muscle spasms
- less severe involvement of hands and feet
- serious disorders of the autonomic nervous system
Prevention
Public education regarding:
- the necessity of complete immunization with the tetanus vaccine (included in the national vaccination schedule or recommended to restore immunity in pregnant women, unprotected adults, or certain occupational risk groups)
- the danger of puncture wounds and closed wounds with tetanigenic potential, and the need for active and/or passive prophylaxis after injury
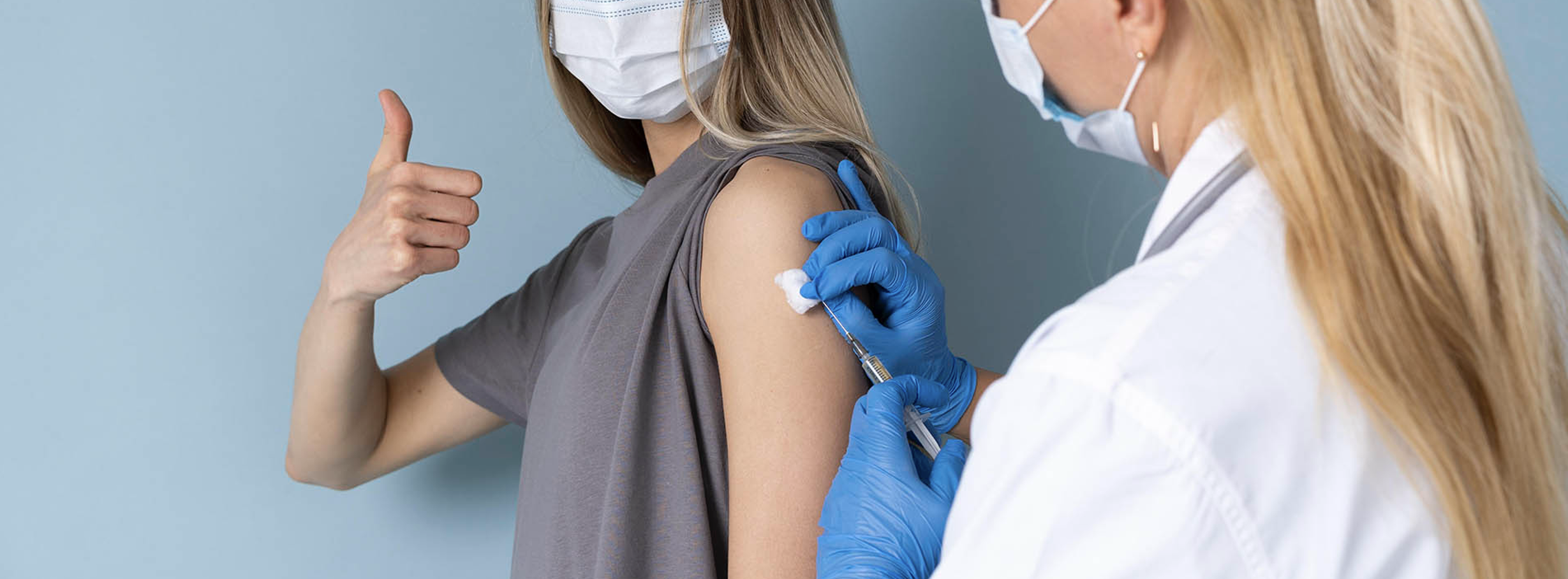
Specific active immunization is done with the tetanus vaccine, which ensures long-lasting protection for at least 10 years if administered according to the official vaccination schedule, followed by a single booster dose (scheduled or as needed).